Nowadays, in the era of digital technology, healthcare is undergoing much change due to electronic health records (EHRs) being used by such a large portion of the population. The traditional paper medical charts in the electronic format have dramatically changed how medical professionals keep patients’ medical data.
In this blog, we’ll deal with electronic health records and the list of the components of these records, benefits, and challenges.
You can also learn about healthcare management by Clicking HERE!
Quick Links
ToggleIntroduction to Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Electronic Health Records, commonly known as EHR includes a digital representation of a patient’s medical record. It includes diagnoses and treatment plans, prescriptions or allergies, as well as testing outcomes.
Contrary to paper-based records, EHRs are real-time safe, and easily accessible data to authorized users. It facilitates smooth communication and coordination between medical professionals through smart health kiosks.
Types of Electronic Health Record Systems

1- Patient Demographics
The core of any EHR is the patient’s details, such as names, addresses, contact details, insurance as well as emergency contact numbers. The data ensures accuracy in the recognition and monitoring of patients throughout healthcare settings.
2- Medical History
EHRs contain comprehensive medical histories which include past medical conditions such as surgeries, vaccinations as well as allergies, and your family’s medical history.
The information provided by EHRs provides healthcare professionals with essential information regarding the health of a patient and helps to create the patient’s treatment plan.
3- Laboratory Results
Integration of laboratory systems allows EHRs to record and display tests for diagnostic results like urine analysis, blood tests as well as imaging studies.
Healthcare providers can quickly access the outcome to monitor patients’ progress, make educated decisions, and modify treatment plans as needed.
4- Medication Lists
EHRs keep up-to-date lists of medications that include prescribed medication doses, frequency as well and refill information.
This can prevent the occurrence of medication errors, interactions and unwanted reactions with a thorough summary of the patient’s present and previous medication.
5- Treatment Plans
EHRs assist in the design and administration of treatment plans such as prescribed medicines, treatments, and procedures as well as subsequent appointments. Healthcare providers can collaborate with these plans to ensure the continuity of treatment and adherence.
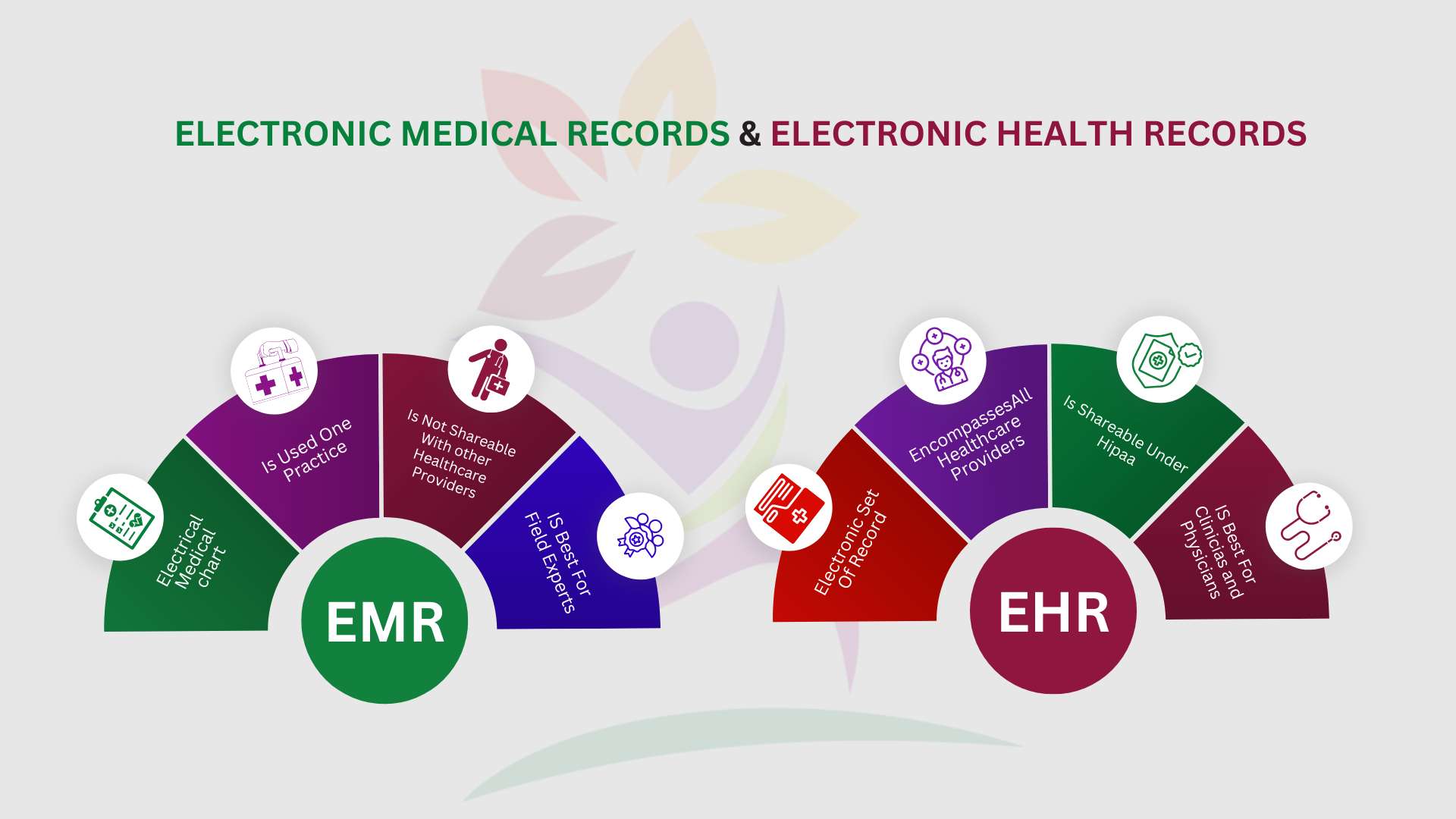
Comparison of EHR as well as EMR

Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) are frequently used interchangeably but there are distinct contrasts.
Both systems digitalize the health records of patients, EHRs go beyond the boundaries of healthcare institutions. It brings an extensive understanding of a patient’s medical background through several healthcare providers and settings.
Benefits of Electronic Health Records
1- Improved Patient Care
EHRs aid in coordinated health care by providing healthcare professionals immediate access to pertinent information about the patient, which allows for prompt diagnosis, timely treatment intervention, and preventive health strategies.
Patients gain from improved messaging, less wait time, and improved safety by providing warnings about allergies, drug interactions, and indications for treatment.
2- Enhanced Efficiency
Moving from paper-based records to electronic records will eliminate manual procedures like file filing, retrieval and transcription.
3- Better Data Management
EHRs allow the gathering of storage and analysis of massive quantities of data from patients and data, opening the role of healthcare management for the population as well as clinical research and improvements in quality.
Data analytics tools can identify patterns, trends, and outliers. They allow healthcare institutions to make informed decisions based on data to boost results.
Implementation of Electronic Health Records Systems
Incorporating the EHR system is a process that requires meticulous planning, stakeholder engagement and strategies for managing change to warrant an easy transition process and maximize the gains.
Healthcare providers must consider the technical aspects, including the compatibility of systems, data migration as well as comparison and cybersecurity in addition to addressing culture and workflow concerns.
Examples of Electronic Health Records Systems
1- Records Systems
Many Electronic Health Records systems are extensively used in health care settings with distinct features and functions that are specifically designed to meet the requirements of different practices and specialties situations. Examples include:
2- Epic Systems Corporation
The company is known for its extensive EHR solutions utilized by big hospitals and medical academic centers. It offers features like integrated workflows for clinical care and decision-support tools and portals for patient engagement.
3- Cerner Corporation
Cerner Corporation: EHR solutions to boost efficiency in clinical and operational processes across a range of healthcare environments. It offers modules to benefit from electronic health records managing the revenue cycle as well as population health management and much more.
4- Allscripts Healthcare Solutions
Provides a variety of EHR products that cater to the demands of small to medium-sized practices, as and large-scale healthcare institutions. Offers custom EHR solutions that include features including e-prescribing and clinical decision support, as well as interoperability features.
Medical Technology
Offers integrated EHR solutions to be used in smart care hospitals ambulatory settings and various other healthcare institutions. It is renowned for its user-friendly interface, interoperability functions and assistance to make clinical decisions.
Pros and Cons of Electronic Health Record
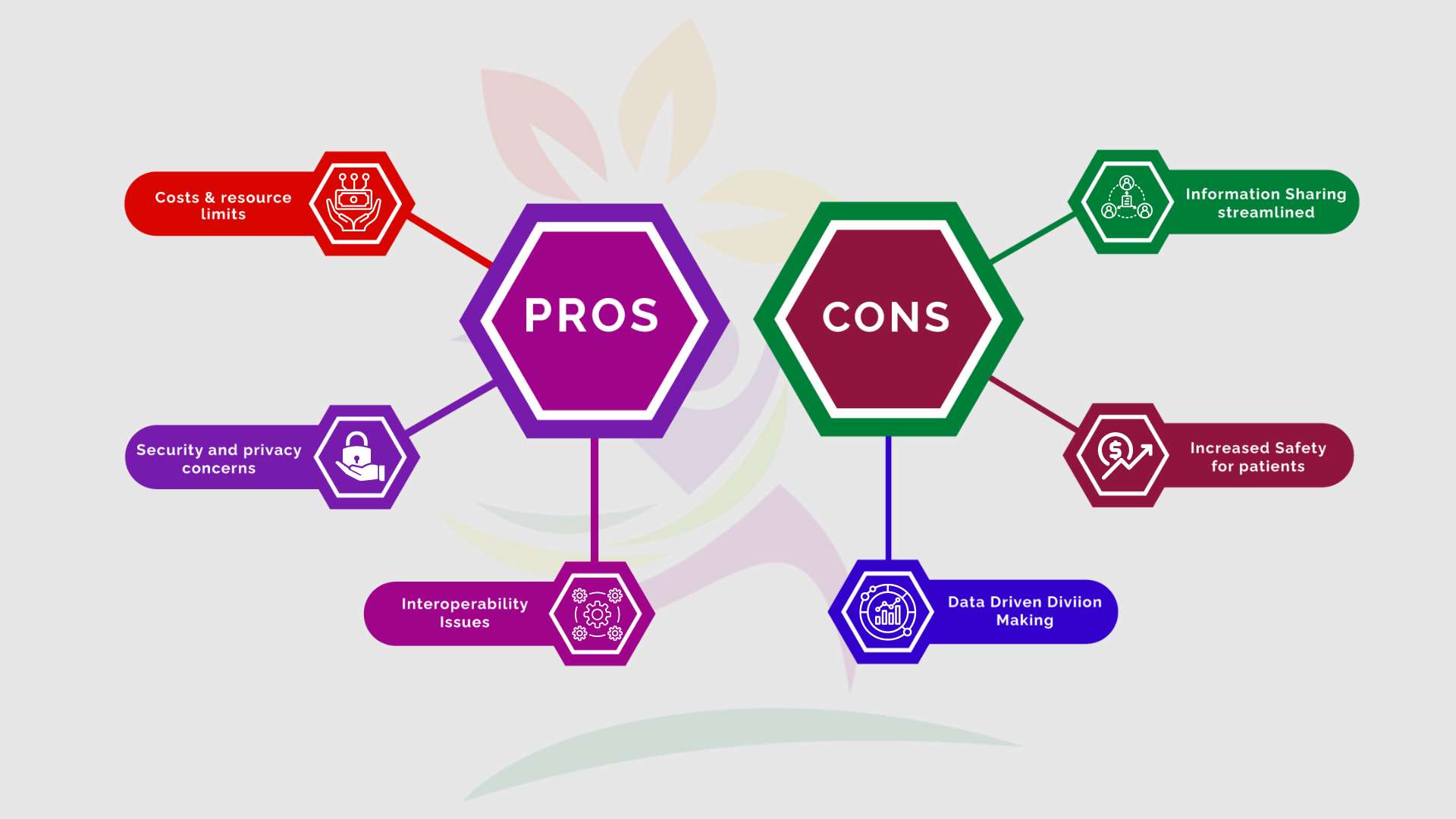
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Information Sharing Streamlined | Costs of Implementation and Limitations on Resources |
| Increased Safety for Patients | Security and Privacy Concerns |
| Improved Productivity and Efficiency | Disruptions to Workflows and Opposition to Change |
| Data-driven Decision-Making | Interoperability Issues |
| Better Payment and Reimbursement Procedures | The Burden of Documentation on Healthcare Providers |
Advantages
● Information Sharing Streamlined:
Allows quick and easy access to the patient’s records for licensed healthcare professionals.
It facilitates smooth communication and coordination between the various health professionals who are involved in the care of patients.
● Increased Safety for Patients:
Lowers the chance of making mistakes caused by handwriting that is not clear or paper documents that are lost.
Healthcare providers are informed of potential allergic reactions or interactions with drugs to increase the security of medication.
● Improved Productivity and Efficiency:
Automates mundane tasks, such as appointments and refills which saves time for health professionals and patients.
Facilitates faster recording and the retrieval of information about patients This payoff in faster and faster workflows in the clinical setting.
● Data-driven Decision-Making:
Gives you access to all of the patient’s details, including medical histories as well as results of tests, results as well as treatment plans. This allows medical professionals to make more informed choices.
Facilitates evidence-based practice and research by providing large databases to study.
● Better Payment and Reimbursement Procedures:
It streamlines documentation and coding to reduce billing errors while ensuring accurate reimbursement.
Allows for timely filing of claims. Also, it allows electronic billing to speed up billing and payment cycle control.
Disadvantages
● Costs of Implementation and Limitations on Resources:
The cost of initial set-up associated with electronic health records (EHR) Systems can be significant. This includes hardware, software, as well as the cost of training.
Maintenance and upgrade projects on a regular basis could be expensive, particularly for smaller health centres.
● Security and Privacy Concerns:
Electronic health records are vulnerable to security breaches, data leaks and improper access, which raises concerns about the security of patient information.
Compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is vital, but it can be challenging to ensure.
● Disruptions to Workflows and Opposition to Change:
Moving from paper-based systems to electronic methods can interrupt workflows, and will require some time to adjustments.
Certain healthcare professionals may be resistant to EHRs because of concerns regarding changes to work procedures or perceived diminished autonomy.
● Interoperability Issues:
EHR systems of different manufacturers could not communicate seamlessly with each other, leading to problems with interoperability.
Insufficiently standardized formats for data and protocols could hinder the transfer of information about patients across different healthcare institutions.
● The Burden of Documentation on Healthcare Providers:
Maintaining and logging electronic health records is lengthy, leading to a rise in the burden of documentation on health professionals.
Information entry procedures can distract patients from their direct care, and cause burnout for providers.
Future Trends in Electronic Health Records
In the future, Electronic Health Records promise continued advancement and innovation driven by technological advances, regulatory demands, and changing healthcare models.
The most important trends are the use of AI, standards for interoperability of integrated telehealth systems, and patient-centric designing principles.
Role of (EHR) Electronic Health Records in Pakistan
| Aspect | Country Response | Year Introduced | Percentage/Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| National EHR System | Yes | 2013 | |
| Legislation Governing National EHR System | Yes | ||
| Health Facilities with EHR | |||
| – Primary Care Facilities | Yes | 25-50% utilization | |
| – Secondary Care Facilities | Yes | 25-50% utilization | |
| – Tertiary Care Facilities | Yes | 25-50% utilization | |
| Other Electronic Systems | |||
| – Laboratory Information Systems | Yes | 35% utilization | |
| – Pathology Information Systems | No | 18% not implemented | |
| – Pharmacy Information Systems | Yes | 33% utilization | |
| – PACS | No | 26% not implemented | |
| – Automatic Vaccination Alerting System | No | 10% not implemented | |
| ICT-assisted Functions | |||
| – Electronic Medical Billing Systems | Yes | 58% utilization | |
| – Supply Chain Management Information Systems | No | 58% not implemented | |
| – Human Resources for Health Information Systems | Yes | 69% utilization |
The statistics provided are sourced from the World Health Organization (WHO) for Pakistan’s healthcare infrastructure. These metrics reflect the WHO’s assessment of electronic health record (EHR) systems and related electronic infrastructure within the country.
Pakistan is rapidly advancing in AI telemedicine, with Fitwell Hub emerging as the largest telehealth ecosystem startup in the country, offering a comprehensive platform for healthcare delivery. It offers a cloud-based Electronic Health Record (EHR) system alongside telemedicine services, enabling healthcare providers to offer remote consultations and manage patient records efficiently. Fitwell Hub aims to revolutionize healthcare accessibility and delivery in Pakistan by leveraging technology to connect patients with healthcare professionals seamlessly.
Conclusion
Electronic Health Records have emerged as a key element of the modern delivery of healthcare providing providers with complete information that is accessible and useful data about patients.
Although EHRs add many benefits concerning enhanced health care, efficiency as well and data management the implementation and improvement need careful planning, cooperation, and constant investment.
Technology continues to advance and the healthcare system adapts to evolving requirements, Electronic Health Records will remain a key component in delivering top-quality integrated care.
Need To Know More? Click HERE
SUMMARY
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have transformed healthcare by replacing paper records with digital systems, ensuring real-time, secure, and accessible patient data. They facilitate better communication among healthcare providers, improving patient care and operational efficiency.
Key Components of EHRs
- Patient Demographics – Stores personal and contact details for accurate identification.
- Medical History – Includes past conditions, surgeries, allergies, and family history.
- Laboratory Results – Integrates diagnostic test results for quick decision-making.
- Medication Lists – Maintains prescriptions, dosages, and refill information.
- Treatment Plans – Documents ongoing care, follow-ups, and medical procedures.
EHR vs. EMR
EHRs provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history across multiple providers, unlike Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), which are limited to single institutions.
Benefits of EHRs
- Improved Patient Care – Enables timely diagnoses, preventive care, and treatment adjustments.
- Enhanced Efficiency – Reduces paperwork, streamlines workflows, and minimizes errors.
- Better Data Management – Facilitates research, analytics, and data-driven decision-making.
Challenges of EHR Implementation
- High Implementation Costs – Requires investment in hardware, software, and staff training.
- Security and Privacy Risks – Vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Interoperability Issues – Inconsistent data formats hinder information exchange.
Future Trends in EHRs
Technological advancements, AI integration, interoperability standards, and telehealth solutions will shape the future of EHRs, enhancing healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
EHR Adoption in Pakistan
Pakistan has made significant progress in EHR implementation, with Fitwell Hub leading in AI-driven telemedicine and cloud-based EHR systems. It bridges the gap between patients and healthcare providers, revolutionizing medical accessibility in the country.














